When it comes to vaccines, India has worked diligently to make a name for itself. It is the world's largest supplier of vaccines, producing 62% of global demand. Since 2012 India's pharmaceutical industry market value has been growing significantly. The vaccine storage temperature and cold chain logistics play a large role in how India is able to safely deliver life-saving vaccines all across the globe.
There have been great strides around the world in the development of vaccines in the last 60 years. Currently, there are vaccines to prevent 20 life-threatening diseases. Through the help of the World Health Organization (WHO), there is a global outreach to bring vaccines to poorer countries where preventative healthcare isn't as readily accessible. By reaching these underserved areas, it helps prevent infectious disease outbreaks on a global level.
The establishment of the Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP), first adopted in 1978 and adapted several times over the years, developed a vaccine protocol for children, with a recommended schedule for high life-threatening, extremely high life-threatening, moderate life-threatening, and low life-threatening potential diseases. With the establishment of the National Rural Health Mission in 2005, the community outreach for administering vaccines to the rural and underserved areas has improved.
According to McKinsey, in 2012, India's pharmaceutical market share was less than desirable at $ 500 million. At that time, nearly two million Indian lives were lost per year, most of which were children due to vaccine-preventable deaths. India saw an opportunity to right a wrong for its citizens and improve business opportunities throughout the country.
Through the increase in vaccine development and outreach programs, the Indian vaccine industry grew significantly, having reached nearly $ 1.3 billion in 2019.
India is the largest manufacturing region for vaccines worldwide. Currently, two-thirds of its production is exported, while one-third is used domestically, with the UIP helping to distribute the vaccines countrywide. While production has grown significantly, the Indian pharmaceutical industry is expected to climb to 65 billion USD by 2024.
India's low cost of production, research and development contribute to the country’s cost efficiency of not only vaccines but all their pharmaceuticals. According to investindia.gov, producing pharmaceuticals in India is 33% less costly than that of western markets. Their ability to keep costs down directly correlates to their high export numbers making vaccines obtainable for even the poorest of populations.
India is the world's largest manufacturing region and exporter of generic medicines. It contributes 60,000 generic brands within 60 therapeutic categories, exporting approximately two-thirds of all its supplies to countries worldwide.
Their generic drug industry is being threatened due to strict regulations being placed on exports of medicinal products. In August of 2020, President Trump signed an executive order disallowing drug imports, both as active ingredients and formulations. While France and Germany appear to be heading in the same direction. For now, India remains the leading manufacturing market in the generic drug industry.
The world has watched as India thrived in the world of pharmaceuticals, but China has not only taken note but also decided they need a piece of the market. Beijing's "Made in China 2025" has included pharmaceuticals as part of its targeted campaign.
India's claim to fame is its ability to manufacture and export affordable medications across the globe, particularly to the most impoverished countries.
Fortunately, it is currently believed that China will maintain its efforts to establish itself as a formulator of pharmaceuticals leaving India to rule the generic medication field. But with both vying for raw products, there is some concern that it might drive up the cost of production, edging out India's lead on the affordable healthcare market.
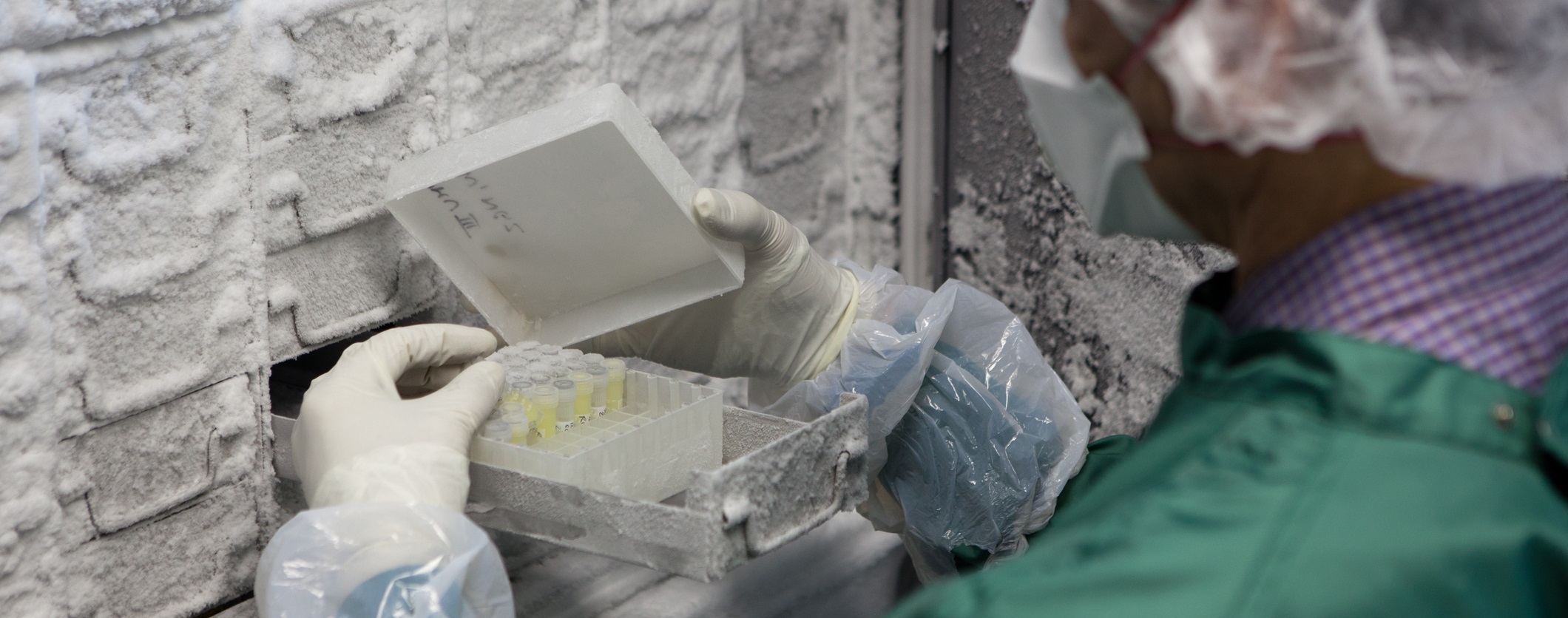

The vaccine storage temperature must be closely managed and controlled to maintain the vaccine’s efficacy. Some vaccines are more susceptible to heat, such as the measles and DTP vaccines, and others are more cold-sensitive such as Heb B and Hib (in liquid form). Once its viability is lost, it cannot be restored.
Since most of India's vaccines are exported to other countries, maintaining a correct vaccine storage temperature during transport is of the highest importance. Vaccines have a short shelf-life, so shipping by air is a preferred means of transport for many vaccine manufacturers. To ensure that shipments arrive safely and intact, air freight supply chain stakeholders follow strict vaccine storage and handling requirements as defined by the shipper/manufacturer in the cold chain process. Vaccines' active ingredients may lose potency or even be destroyed if the temperature is not maintained between (2℃–8℃), or -20°C for some products, so the vaccine cold or frozen storage and transport system is essential across the supply chain.
Stakeholders have the responsibility of identifying and mitigating the risk of damage to vaccine shipments within the cold chain logistics. They should each make sure that the vaccine storage temperature is well maintained at every step of the way while the consignment is in their area of responsibility. This applies to all critical control points and stakeholders in the process from manufacturing to patient, including all important air freight supply chain stakeholders like forwarders, ground handling agents, airlines, warehouse operators and trucking vendors.
Maintaining strict vaccine storage, handling and transport requirements for cold chain logistics is how vaccines can be shipped effectively worldwide. Even though the roles may differ, the same quality and risk management principles must be followed no matter where a stakeholder may be in the cold chain supply chain. Stakeholders involved should always follow, good storage practices (GSP), and good and distribution practice (GDP).
Manufacturers
The vaccine supply chain begins with the manufacturers. It is their responsibility to properly prepare the vaccines for shipment. This not only includes appropriately packaging and labeling of vaccine shipments for cold or frozen storage, it also means ensuring all documentation is in order so there are no issues with customs or foreign state requirements, allowing the vaccines to arrive in a timely manner
Freight Forwarders
The freight forwarders are responsible for selecting and engaging only those subcontractors that are approved and have a required knowledge and quality and risk management systems in place for safe handling and transport of vaccines.
Vendors offering temperature-controlled road transport meet vaccine storage and handling requirements by carrying the vaccine cold storage at predefined and communicated temperature range and set points to ensure product safety and efficacy. The qualified temperature-controlled trucks are an essential part of the cold chain logistics enabling vaccines to safely move between the supply chain points.
Airlines
It is the airlines who will do most of the worldwide shipping. Shipping by air allows vaccines to reach distant destinations in a timely manner. This is crucial since the shelf-life of many vaccines is short-lived. Airlines must adhere to the vaccine storage and handling requirements before, during, and after the flight between transfers with the freight forwarders.
Once received from the freight forwarders, the vaccines must be stored in qualified temperature-controlled storage premises at the airlines’ or ground handling service providers facilities while waiting for aircraft loading to commence. During this time, the shipment will be cross-checked for all relevant safety requirements, such as checking appropriate labels, checking the air waybill, temperature-controlled instructions and overall condition of the shipment before making it ready for carriage. This is managed by using IATA mandatory check list for time and temperature sensitive products. Considering the process duration, exposure to external temperature conditions needs to be minimized and wherever possible, maintained at the predefined temperature range.
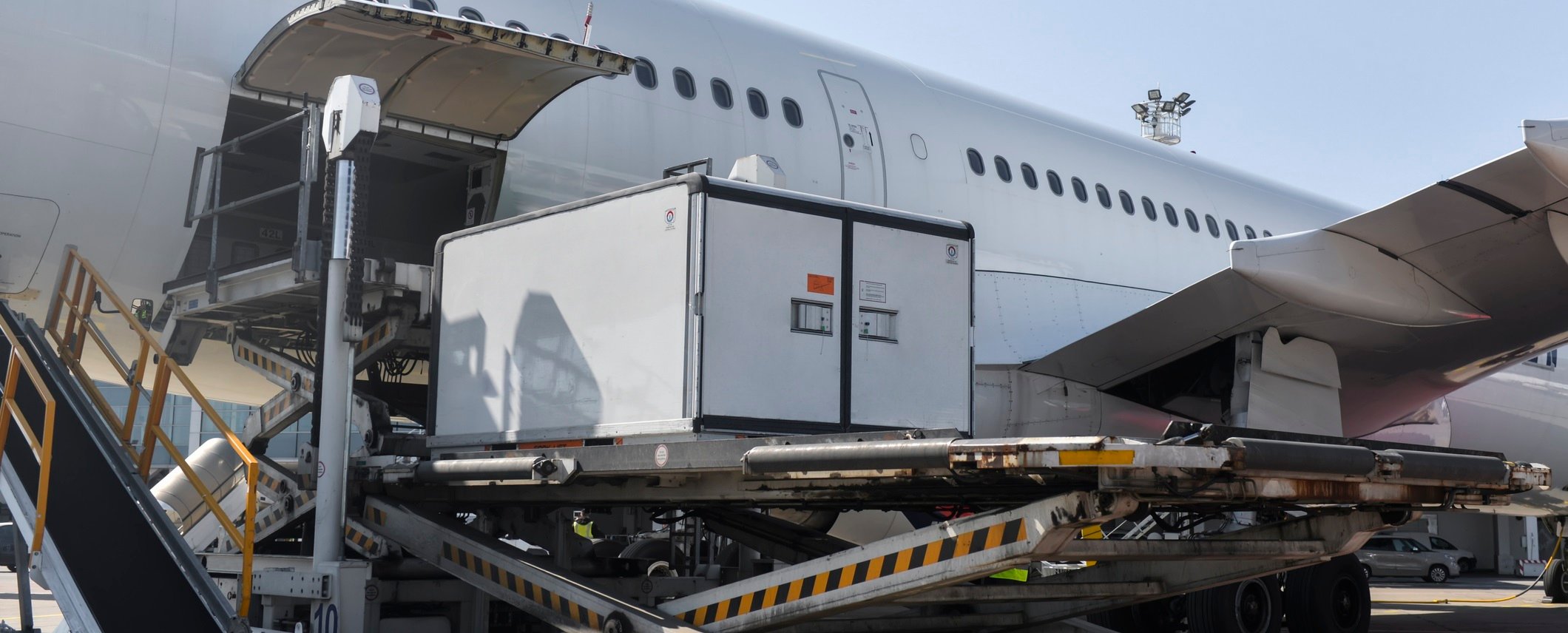

There is no doubt that the effects of COVID-19 have been considerable and challenging for the airline industry. Airlines saw a loss of cargo tonne-kilometers (CTK) of 21.4% year-on-year in 2020. While the air cargo industry was hit hard, it performed significantly better than the passenger side of the business. The loss of revenue passenger kilometers (RPK) presented a significant problem for air cargo as it caused a shortage of available cargo space needed to deliver shipments across the globe.
Even with the pandemic in full swing during 2020, India still maintained its pharmaceutical supply chain.
With the creation of COVID-19 vaccines, the need to ship them worldwide became a priority. This meant airlines play an essential role in transporting billions of doses of the vaccines quickly and safely around the globe.
It is important to follow the rules and recommendations in IATA Temperature Control Regulations Manual (TCR) for temperature-controlled and time sensitive pharmaceutical products such as vaccines. Vaccine cold storage is vital to the efficacy of vaccines that prevent life-threatening diseases while they are being shipped all across the world. Cold chain logistics has a role in helping to save lives. The standardized rules and regulations keep the process in check for manufacturers, freight forwarders, and airlines alike, assuring the highest quality possible.
The transportation of time and temperature-sensitive shipments such as vaccines must meet pharmaceutical manufacturers' requirements. To comply with these requirements, IATA has established a CEIV Pharma training and certification program to help properly train stakeholders on consistently meeting the proper standards of handling pharmaceuticals. The IATA CEIV Pharma program provides transport companies an independent audit/certification to ensure their processes and procedures for transporting temperature-controlled shipments are in line with regulations and best practices.
For information regarding the rules and regulations for temperature-controlled substances, including vaccines and other pharmaceuticals, please refer to IATA Temperature Control Regulations Manual.