
In 2019, the global export of pharmaceuticals was reported at US $392.9 billion, and it has reached over $1 trillion since then, proving that it is a growing market. According to statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Parenteral Drug Association (PDA), pharmaceutical organizations spend an average of 6% of their revenue on logistics. This is to protect against widespread losses of pharmaceuticals due to improper temperature during storage and shipping, which can be even more costly.
Due to increased demand, the pharmaceutical trade has grown significantly. Many pharmaceuticals have to be kept within a specific temperature range from Deep Frozen at-18C to simply refrigerated at 8C to maintain their efficacy. This means that exporting globally time and temperature are crucial. Shipping by air allows for the speed needed to deliver the pharmaceuticals quickly and safely to their destination anywhere in the world. Airlines strictly follow IATA Temperature Controlled Regulations (TCR), ensuring that everyone's needs are met to keep up with market demands.
Temperature controlled air cargo includes perishables such as pharmaceuticals. According to IATA's Temperature Controlled Regulation Manual, "pharmaceutical products are defined as substances intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or cure of diseases". Pharmaceuticals can be divided up into subcategories such as biological products, drug products, homeopathic remedies, herbal products, and medical devices. The pharmaceuticals come in a wide array of forms, such as aerosols, capsules, injections, creams, syrups, just to name a few.
Some pharmaceutical products will fall under the category of dangerous goods. If this is the case, all necessary precautions must be followed and the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (IATA DGR) will supersede the Temperature Control Regulations (TCR).

Temperature controlled air freight is made up of perishable items; while most of this is pharmaceuticals, such as, vaccines, there are other types of temperature controlled air cargo as well. Tree-ripe fruits, sliced fruits, and salads are all time and temperature-sensitive that cannot be shipped by ground transportation like unripe fruit. But by and large, pharmaceuticals are what dominate temperature controlled shipping.
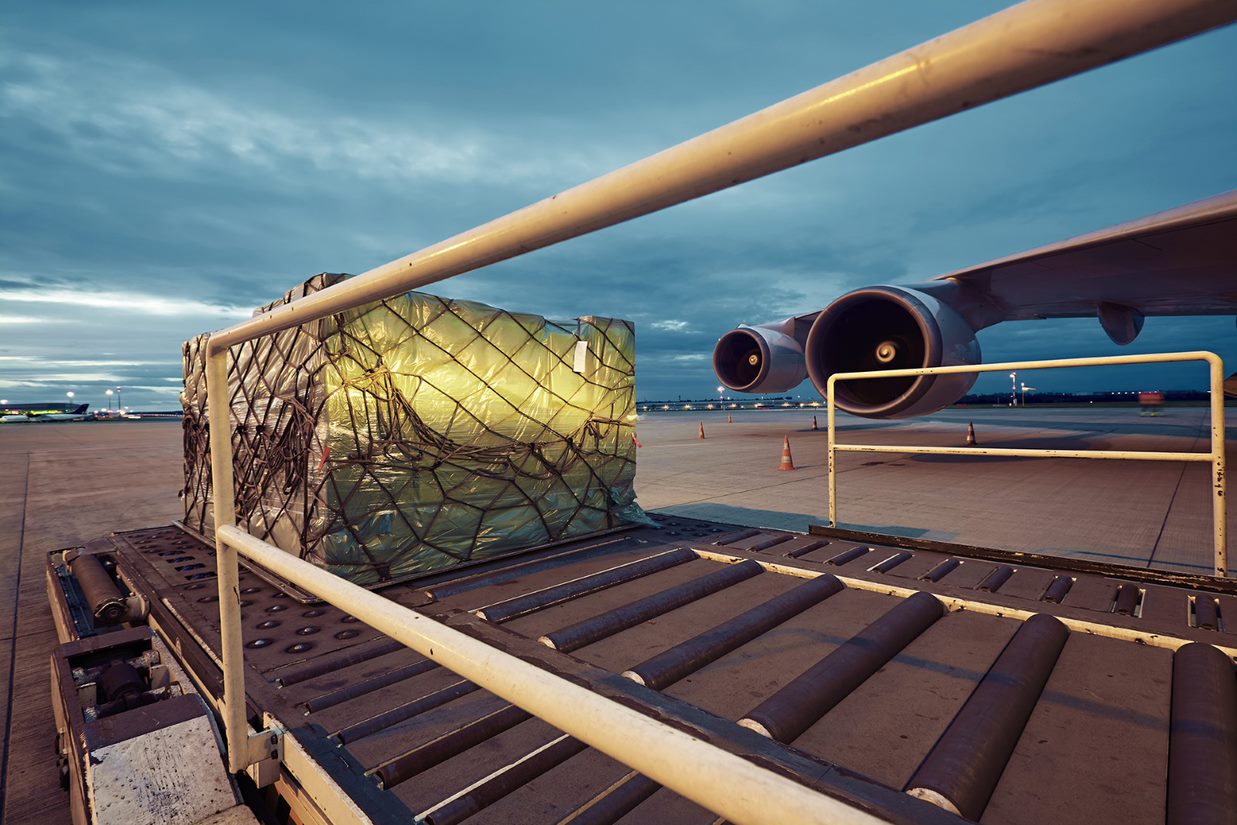
Transporting temperature controlled shipping by air seems like the logical choice due to its time-saving nature, but that is not the only factor to consider. Temperature controlled shipping by air versus by sea is more expensive. However, under certain circumstances, time trumps cost. In such instances as clinical trials or radioactive medicine where time is crucial, shipping by air is necessary. Radioactive pharmaceuticals can become less effective over time due to the half-life of medication.
Another example where shipping by air is preferred is when there are large batches of vaccines that need delivery. Transporting smaller shipments by air versus transporting large consignments by sea provides a certain assurance against substantial losses. If something were to go wrong with a large ocean shipment, the financial damage would be disastrous. Shipping temperature controlled substances by air allow for better control of the cold chain processes.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers are looking for transporters who can deliver their products quickly and safely with little or no incidents that would result in the loss of their product directly or which would affect their efficacy once in use. Logistics is crucial in ensuring the cold chain is not broken so that all regulations are followed and the temperature-controlled air cargo is delivered as intended.

The cold chain begins with the manufacturers. How the pharmaceuticals are packaged is crucial to arriving at their destination securely. With 47% of perishables being shipped from tropical or warmer climates having suitable containers that can be held in such conditioners is essential. Insulated or refrigerated containers should always be used to ensure the proper temperatures can be maintained as commodities are stored, handled, and shipped.
Airport ground operation personnel are instrumental in the cold chain procedures. Aircraft turnaround time plays an essential factor in getting pharmaceuticals delivered on schedule. Handlers cover the pre-conditioning and post-conditioning of all temperature controlled air cargo.
“Aviation industry, like Pharmaceutical manufacturing is a highly regulated industry. Shippers thus expect involved business entities to design Quality and Risk Management Systems in accordance with global regulatory requirements, industry best practices and specific shipper – product requirements.”
Zvonimir Majic Ph. D.
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Director Global Quality Logistics
A critical control point is a step or procedure where a rule or practice can be implemented to prevent errors or risk to a critical level. When it comes to IATA's Temperature Control Regulations there are several critical control points to protect from such occurrences. These control points include:
Quality management systems are guidance given in addition to the rules and regulations. It pertains to information regarding training, procedures, management, and related topics to support good practices in maintaining proper protocols for handling temperature-controlled substances. According to IATA's Temperature Control Regulations (TCR), a sound quality management system should include the following:
Standard Operating Procedures is an internal document that provides clear-cut instructions on how personnel and teams will perform job-related tasks. Throughout the cold chain process, specific SOPs should be followed to ensure the quality of the pharmaceuticals is delivered safely and with its high quality maintained during the temperature controlled shipping.
Corrective and preventive action is part of the Quality Management Systems. Periodically senior managers should review the quality system to make sure that it remains relevant and effective. When changes are necessary, they are implemented through corrective and preventive action (CAPA), and control procedures are changed.
CAPA involves investigating, understanding and correcting inconsistencies while implementing changes to prevent future complications.
“One of main focal points in audits by the Pharma manufacturing industry is the Systematic Root Cause Analysis as a part of Non Conformity Reporting and risk management driven CAPA process. These components as standard part of vendors QMS are establish in an effort to prevent risks becoming a root cause in shipping TTSPP shipments.”
Zvonimir Majic Ph. D.
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Director Global Quality Logistics
Quality Management Systems requires frequent audits to ensure that the system is being adequately followed and standards met. IATA created the Center of Excellence for Independent Validators in Pharmaceutical Logistics (CEIV Pharma) to help the entire air cargo cold chain go beyond the minimum requirements. CEIV Pharma guidelines supersede the already strict baseline regulations of pharmaceutical norms such as:
Being CEIV Certified is essential as transporting and handling pharmaceuticals is a complicated endeavour.
Being CEIV certified ensures that all staff, facilities,and operations meet the regulations and guidelines of the pharmaceutical manufacturers no matter where it is.
To regulate the industry, becoming certified is necessary, even for trucking companies that transport pharmaceuticals. There is a network of certified approved shippers that are utilized in the transporting of pharmaceuticals, and to be part of that network means becoming CEIV certified. This ensures that the high-level of care is met during the temperature controlled shipping of pharmaceuticals.
To help shippers, agents, and airlines with temperature controlled air cargo, the IATA Live Animal and Perishables Board developed the "IATA Acceptance Checklist for Time and Temperature Sensitive Healthcare Shipments". This checklist helps airlines and ground handling personnel walk through the minimum checks for processing temperature-controlled substances.
The airline industry took a drastic hit due to COVID-19. Due to air travel restrictions grounding so many aircraft, the aviation industry saw the most catastrophic damages since World War II. It was the air cargo industry that kept airlines afloat. With the release of COVID-19 vaccinations, the world needed a way to disperse the vaccines around the globe quickly and efficiently, which meant airlines were required to accommodate the massive demands.
This also meant that many new companies started handling and transporting vaccines and as a result, they started following IATA's Temperature Control Regulations (TCR) as well as IATA’s Guidance for Vaccine and Pharmaceutical Logistics & Distribution which provided the most current and accurate information needed for stakeholders.
IATA's rules and regulations is an industry-standard set of guidelines compiled into an easy-to-read manual to assist stakeholders in doing their job to the very best of their ability. It contains all the pertinent information needed to safely handle and ship temperature controlled air freight worldwide while complying with all mandatory requirements.
IATA's temperature-controlled rules and regulations are extracted from the Perishable Cargo Regulations (PCR) as the guidelines are very particular to pharmaceuticals, including vaccines which recently took center stage, and need even more meticulous care. The Temperature Control Regulations (TCR) is published every year to provide the most current information under the authority of the IATA Cargo Services Conference and is updated by the Live Animals and Perishables Board (LAPB) and with input from Time and Temperature Working Group (TTWG).
IATA's Temperature Control Regulations (TCR) are necessary for a shipper, freight forwarder, ground handler, or airline. It will assist you in compliance with all mandatory regulations in the transport of pharmaceuticals and all other temperature controlled air freight. You can find more information in the Temperature Control Regulations (TCR). It is recommended to become certified in the industry standards with the CEIV Pharma program. IATA provides all the necessary tools to meet the demands of a complicated process.